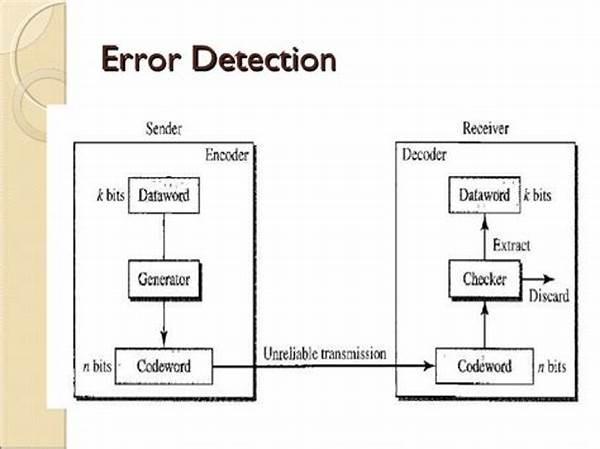
In today’s fast-paced digital world, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data is more crucial than ever. Whether you’re a software developer, data analyst, or someone who just wants to streamline your workflow, sharpening your error detection skills is key. There’s an art to identifying errors early, and strategies for error detection help you catch problems before they escalate. Embracing effective methodologies not only enhances efficiency but also boosts confidence in your work’s quality.
Understanding the Importance of Error Detection
Identifying errors early in any process can save tremendous amounts of time and resources. Strategies for error detection are not merely about identifying when something goes wrong but understanding why it happened and how to prevent it. These strategies involve a mix of techniques, from manual reviews to automated systems, each bringing their own strengths to the table. For instance, manual code reviews are essential in software development, where a keen eye can catch nuances that automated systems might overlook. On the flip side, automated tools are excellent for handling large volumes of data, providing a backbone to any comprehensive error detection strategy. Combining both approaches ensures a robust mechanism that can handle various kinds of errors efficiently.
Incorporating strategies for error detection at the earliest stages of a project can preemptively address potential issues. When embarking on a new task, developing a keen eye for detail is vital. However, it’s not just about finding errors but understanding the underlying cause to implement effective long-term solutions. This involves training and experience, learning from past mistakes, and adapting your approach to new challenges. As teams become more adept at applying these strategies, they can achieve better results, reduced downtime, and improved overall performance.
Effective Techniques in Error Detection
1. Regular Audits: Conducting regular audits is one of the most reliable strategies for error detection. They help ensure that processes remain consistent and errors are caught early.
2. Automated Testing: Leveraging automated testing tools provides consistent error detection across vast datasets, reducing reliance on manual inspections.
3. Peer Reviews: Engaging in peer reviews brings fresh perspectives, often revealing errors that can be missed by someone familiar with the material.
4. Data Validation: Implementing data validation processes ensures that only clean, correct data progresses through your systems, minimizing downstream errors.
5. Feedback Loops: Establishing feedback loops not only facilitates quick error detection but also enables teams to learn and prevent similar issues in the future.
Implementing Technology in Error Detection
As technology evolves, so do the methods we use to detect errors. Strategies for error detection have become increasingly reliant on advanced technological solutions. Implementing these solutions requires a blend of cutting-edge tools and keen human insight. Machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence have fundamentally changed the landscape, allowing systems to learn from errors independently. These technologies can identify patterns and anomalies faster than traditional methods, offering invaluable assistance in error detection.
However, tools alone are insufficient for comprehensive error detection. Human oversight remains crucial. Strategies for error detection thrive on the synergy between technological aids and human intervention. For instance, while a machine learning algorithm might flag an anomaly, a human expert determines its significance and decides on the next steps. Thus, successful error detection requires both the precision of machines and the judgement of human experts. This combination ensures a holistic approach, effectively minimizing errors and enhancing the reliability of outcomes across various applications.
Best Practices for Error Detection Strategies
1. Understanding Context: Recognize the context of data and processes to better apply strategies for error detection that are relevant and effective.
2. Integrating Systems: Cohesive integration of different system components ensures a smooth error detection process, minimizing conflicts and redundancies.
3. Continuous Monitoring: Regular system monitoring allows for real-time error detection, enabling swift responses to emerging issues.
4. Training and Development: Continuous staff training ensures teams are up-to-date with the latest error detection methods and tools.
5. Documentation: Meticulously documenting processes and errors enriches the organization’s knowledge base, offering insights for future projects.
6. Cross-functional Collaboration: Working across teams fosters a holistic approach to error detection, incorporating diverse insights and expertise.
7. Scenario Analysis: Performing scenario analyses prepares teams for potential errors and enhances strategic planning.
8. Prioritizing Data Security: Safeguarding data integrity is crucial in error detection, ensuring errors don’t compromise sensitive information.
9. Scalability Considerations: Designing systems to handle increased loads effectively addresses error detection challenges as operations scale.
10. Iterative Improvements: Regular updates to error detection strategies help organizations keep pace with evolving technology and new insights.
Challenges in Implementing Error Detection Strategies
Even with comprehensive strategies for error detection in place, organizations face numerous challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the sheer diversity of errors that can occur. From minor data entry mistakes to significant technical faults, each error type requires a tailored approach for detection and resolution. This vast variety makes it challenging to develop a one-size-fits-all strategy.
Moreover, the pace of technological advancement means that strategies must continually evolve. As systems grow more complex, keeping up with the latest tools and methodologies becomes arduous. It’s not just about adopting new technologies but integrating them seamlessly with existing processes. This requires foresight, adaptability, and a commitment to ongoing learning. Additionally, engaging stakeholders across different levels ensures that strategies for error detection receive the necessary support and resources to be effectively implemented.
The human element also presents a challenge. Training individuals to recognize and respond to errors is vital, yet requires time and investment. Employees must not only learn how to use new tools but also develop critical thinking skills to understand the root causes of errors, making training a significant commitment for any organization.
Creating a Culture of Error Prevention
To ensure effective strategies for error detection, fostering a culture that emphasizes error prevention is crucial. This involves instilling a mindset that views errors not as failures but as opportunities for learning and improvement. Encouraging open communication and collaboration across teams is essential. When individuals feel comfortable discussing mistakes without fear of retribution, they are more likely to contribute valuable insights into improving processes.
A proactive approach to error detection involves regular training and workshops. These sessions not only keep staff updated on the latest strategies but also reinforce a culture of vigilance and attention to detail. Cultivating such an environment not only reduces the incidence of errors but also enhances overall efficiency. Furthermore, recognizing and rewarding efforts to detect and prevent errors can motivate teams to adopt a more meticulous approach to their work, ultimately benefiting both the individuals and the organization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, strategies for error detection form the cornerstone of high-functioning processes across industries. By employing a blend of manual and automated techniques, organizations can efficiently identify and resolve errors, enhancing data integrity and operational efficiency. The approach requires continual adaptation to technological advancements and a deep understanding of the specific challenges within each context. Moreover, investing in training and a supportive culture ensures that teams remain equipped to tackle errors as they arise, transforming potential setbacks into opportunities for improvement. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, so too must the strategies for error detection, ensuring that organizations remain robust, resilient, and ready to meet whatever challenges lie ahead.